Rated Power
To calculate the rated power of the motor, you must first calculate the hydraulic power of the pump:
Note that in the first formula, flow is usually in cubic meters per second and the pressure is in Pascal, and in second formula the flow is in cubic meters per hour and the pressure is in bar.
Ph (kw) = Q (m3/s) x ρ (kg/m3) x ∆h (m) x g (m/s2) = Q (m3/s) x ∆P (Pascal)
or
Ph (kw) = Q (m3/hr) x ∆P (bar) / 36
Ph = Hydraulic Power
- Q = Flow
- ρ = Density
- ∆h = Differential Pressure
- g = 9.81
Then the pump efficiency must be obtained from the pump performance curve (taken from the manufacturer) and if this curve is not available, this efficiency must be estimated experimentally. Through dividing the hydraulic power of the pump by the efficiency of the pump, the BHP power or the brake horse power of the motor (pump absorption power) can be obtained.
BHP (Brake Hoarse Power) (kw) = Ph (kw) / ηp
However, to accurately calculate the motor’s braking horse power (pump absorption power), it can be divided into gearbox efficiency and coupling efficiency (mechanical efficiency) or multiplied by the ambient temperature effect factor and the sea level impact factor.
In the next stage, we divide the obtained BHP by the motor efficiency to get the Rated Power.
Rated Power (kw) = BHP (kw) / ηm
Finally, according to the API 610 standard, Rated Power must be multiplied by the safety factor. This factor can be found in Table 12 of the API 610 standard.
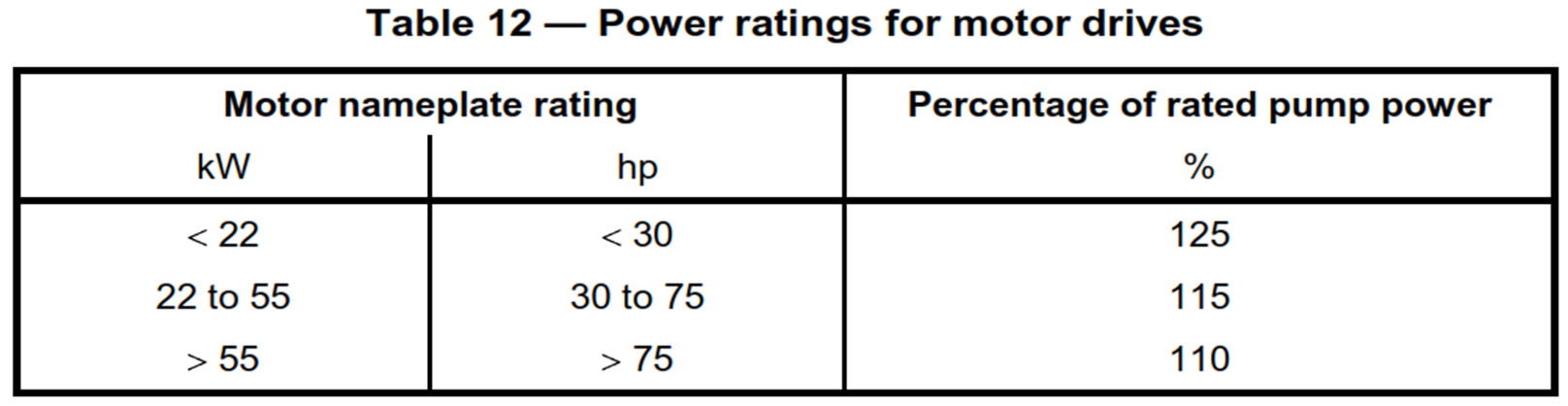
Power rating for motor drivers = Rated Power x Percentage of rated pump power (Table 12 API 610)
