Cooling Water System
The most usage of cooling water is in the bearing house and in the heat exchanger of the flashing system.
In general the needed water cooled for pump can be provided from 2 sources.
- Open-loop cooling water system:
In this way, it is used from site water loop that must have a given temperature and pressure in the inlet and must have a specific pressure in the outlet. For centrifugal pumps in API 610 ANNEX B you can see cooling water system schematic.
- Closed-loop cooling water system:
All the equipment of closed-loop cooling water system shall be assembled on a separate skid. It is recommended to provide the pump and compressor of the cooling water package by pump manufacturer.
6.1.17 The need for cooling shall be determined by the vendor, and the method shall be agreed upon by the purchaser. Fan cooling should be the first choice. If fan cooling is inadequate, one of the plans in Annex B shall be selected. The cooling system shall be suitable for operation with the coolant type, pressure and temperature specified by the purchaser. The vendor shall specify the required flow. To avoid condensation, the minimum temperature at the cooling-water inlet to bearing housings should be above the ambient air temperature. {API 610}
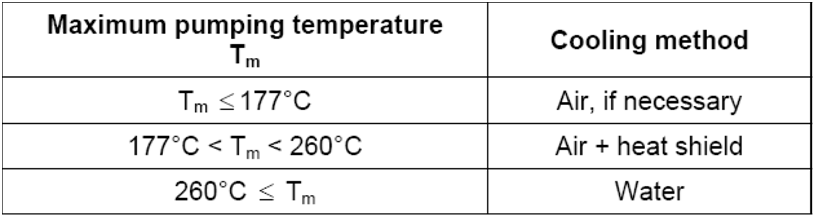
As a minimum bearing cooling shall be provided as follows: {Total}
7.5.1.1 Piping shall be in accordance with ISO 10438 (all parts). {API 610}
7.5.1.2 Auxiliary systems are defined as piping systems that are in the following services: {API 610}
- auxiliary process liquids;
- steam;
- cooling water;
- lubricating oil (see 9.2.6).
7.5.2.7 If heating or cooling is provided, each exchanger component shall be suitable for the process liquid and cooling water to which it is exposed.
7.5.3.1 The arrangement of cooling-water piping shall conform to Figures B.2 to B.7, as applicable.
7.5.3.2 The cooling-water piping shall be designed for the conditions in 6.1.20.
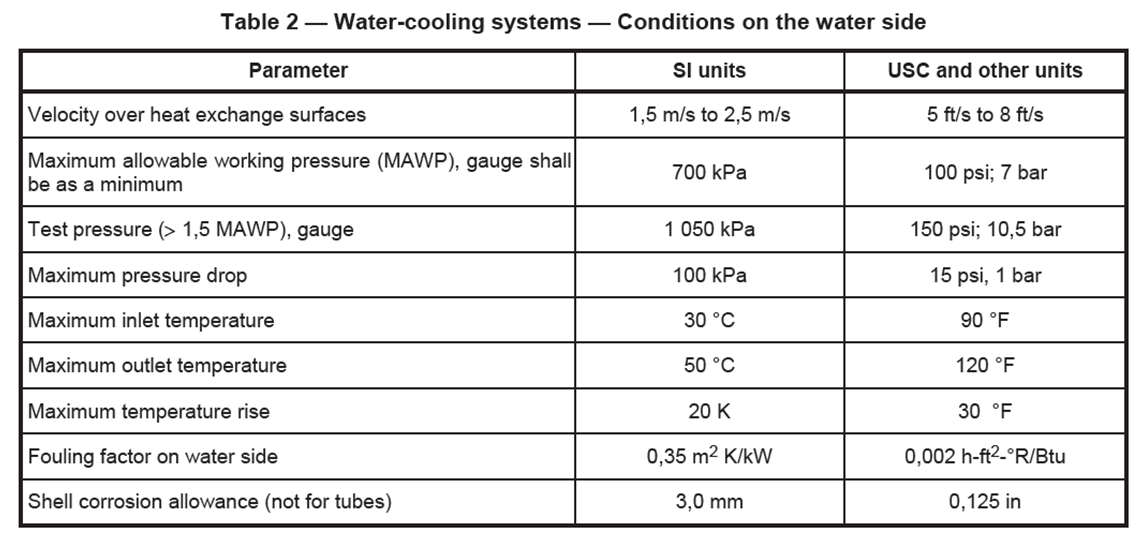
6.1.20 Unless otherwise specified, water-cooling systems shall be designed for the conditions on the water side as given in Table 2.
8.3.2.16 Steam, cooling-water and lubricating-oil piping, if fabricated by welding, shall be tested at 1,5 times maximum operating gauge pressure or 1 050 kPa (10,5 bar; 150 psi), whichever is greater.
Cooling water and lubrication system schematics in annex B of API 610.
Table H.4 — Piping materials for cooling water.
6.10.2.4 Sufficient cooling, including an allowance for fouling, shall be provided to maintain oil and bearing temperatures as follows, based on the specified operating conditions and an ambient temperature of 43 °C (110 °F):
- for pressurized systems, oil outlet temperature below 70 °C (160 °F) and bearing metal temperatures (if bearing-temperature sensors are supplied) less than 93 °C (200 °F); during shop testing, and under the most adverse specified operating conditions, the bearing-oil temperature rise shall not exceed 28 K (50 °R);
- for ring-oiled or splash systems, an oil-sump temperature below 82 °C (180 °F); during shop testing, the sump oil temperature rise shall not exceed 40 K (70 °R) above the ambient temperature in the test cell measured at the time of each reading and (if bearing-temperature sensors are supplied) outer ring temperatures shall not exceed 93 °C (200 °F).
NOTE Pumps equipped with ring-oiled or splash lubrication systems normally do not reach temperature stabilization during performance tests of short duration and sometimes not even in 4 h tests. Temperature-stabilization testing is addressed in 8.3.4.2.1.
6.10.2.5 If water cooling is required, cooling coils are preferred. The coils (including fittings) shall be of nonferrous material or austenitic stainless steel and shall have no internal pressure joints. Tubing or pipe shall have a minimum thickness of 1,0 mm (0,040 in) and shall be at least 12 mm (0,50 in) outside diameter. Water jackets, if used, shall have only external connections between upper and lower housing jackets and shall have neither gasketed nor threaded connection joints, which can allow water to leak into the oil reservoir. Water jackets shall be designed to cool the oil rather than the outer bearing ring.
NOTE Cooling the outer ring can reduce bearing internal clearance and cause bearing failure.
6.10.2.7.1 For pure oil-mist lubrication, bearings and bearing housings shall meet the following requirements.
- Water cooling systems shall not be provided.
6.8.11 If specified, jackets shall be provided on seal chambers for heating. Heating requirements shall be agreed upon by the Purchaser, the Vendor, and seal Manufacturer for high melting point products.
The Supplier shall determine the necessity for seal chamber heating or cooling based on the pump service details as defined in the data sheet and in the project specification. {Total}
4.5.5 Auxiliary pipe connections
When forecast bearing oil temperature is above 80°C, cooling water system shall be provided. {ISO 5199}
Comments:
